Drop Fat Faster with Science-backed Weight Loss Methods
Unlock faster fat loss with these proven, evidence-based weight loss methods.

Key Takeaways
- Your Weightlifting Routine is Crucial
Start with 2-4 sessions weekly, focusing on heavy, compound lifts to maximize fat loss while maintaining muscle mass. - You Must Track Progress Diligently
Regular weigh-ins (weekly or bi-weekly) help ensure your diet and activity levels align with your fat loss goals. - Your Diet Needs to Be Balanced and Sustainable
Prioritize whole foods, reduce junk food, and ensure each meal includes lean proteins. This helps control hunger and maintain energy. - You Should Adjust for Diet Fatigue
Manage diet fatigue by planning maintenance phases every 8-12 weeks and using higher-calorie days to keep energy levels stable. - Your Activity Beyond the Gym is Essential
Hitting 8,000-12,000 steps daily can make a significant difference in achieving single-digit body fat sustainably.
Want to drop body fat while keeping your strength and energy high?
In this expert review, we analyze, critique, and expand on Dr. Mike Israetel's insights into science-backed weight loss methods. With input from a seasoned exercise scientist and over two decades of experience in the gym, we ensure these tips are both realistic and effective.
Why should you listen to us? We break down complicated ideas into simple steps, share practical advice for sustainable fat loss, and include tips to maintain your muscle and enhance your health. Our guide focuses on giving you actionable strategies that fit into your lifestyle.
Continue reading for a fully fact-checked, expert-backed guide that delivers real results. Discover how to transform your body with less fat, more muscle, and improved health.
Related:
- Dr. Mike Israetel on Fat Loss: Losing Weight Effectively
- Caloric Deficit for Cutting: Fat Loss Without Muscle Loss
- How to Gain Muscle & Lose Fat: A 4-Step Process (With Meal Plan)
In a Nutshell: The Path to Single-Digit Body Fat
Your diet is the foundation of your success. Create a sustainable caloric deficit of 250-750 calories per day, prioritize lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains, and track your progress with weekly weigh-ins. Remember, slow and steady wins the race—aim for 0.5 to 1.5 pounds of fat loss per week.
You can make this journey sustainable by planning 8-12 week dieting phases, taking breaks to reduce fatigue, and celebrating small victories along the way. Every step you take gets you closer to your goal, so stay consistent and trust the process—you've got this!
| Key Concept | Main Insight |
|---|---|
| Weightlifting | Preserve muscle mass with 2-4 weightlifting sessions featuring compound lifts. |
| Daily Steps | Achieve 8,000-12,000 steps daily for consistent calorie burn and mobility. |
| Nutrient-Dense Foods | Include protein, fruits, and vegetables in all meals to support fat loss. |
| Caloric Deficit | Reduce daily intake by 250-750 calories to gradually lose fat. |
| Diet Phases | Diet for 8-12 weeks, then take maintenance breaks to manage fatigue. |
| Monitoring Progress | Regular weigh-ins keep you aligned with your fat loss goals. |
Science-backed weight loss methods
Introduction to Body Fat Goals
Setting body fat goals is crucial for anyone seeking a leaner physique. Understanding what constitutes a healthy body fat percentage is the first step. For men, single-digit body fat is typically below 10%. For women, it’s around 17% to 20%. These percentages can vary based on genetics, age, and lifestyle factors.
It's important to remember that body fat isn't the only metric of health. Muscle mass, strength, and overall fitness play significant roles. Striving for a low body fat percentage should not compromise overall health.
Understanding Your Starting Point
Before embarking on a journey to lower body fat, assess where you currently stand. Take note of your body fat percentage and overall fitness level. This will provide a baseline for your progress.
Are you under 15% body fat as a male or 25% as a female? If so, you may be closer to your goal than you think. If you’re significantly above these numbers, it may take time and multiple phases of dieting to reach your target.
Evaluating Your Current Fitness Level
- Track your body fat percentage through methods like DEXA scans, calipers, or bioelectrical impedance.
- Assess your strength and endurance through various physical activities.
- Consider how often you currently exercise and your dietary habits.
Understanding where you are will help you create a realistic plan for where you want to go.
Strategy Number 1: The Importance of Weightlifting
Weightlifting is a cornerstone of any fat loss strategy. It builds muscle, which in turn boosts metabolism. When you lift weights, you're not just getting smaller; you're preserving muscle mass while losing fat. This means a healthier and more aesthetically pleasing physique.
Focus on compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are highly effective. They help maximize calorie burn while building strength.
How to Get Started
- Begin with two to four weightlifting sessions per week.
- Start with one or two sets per exercise and gradually increase.
- Focus on compound lifts rather than isolation exercises.
Don’t rush. Allow your body to adapt and recover. As you progress, you can increase the intensity and volume.
Strategy Number 2: Increasing Physical Activity Levels
In addition to weightlifting, increasing your overall physical activity is essential. A moderate to high level of daily activity supports fat loss while maintaining muscle. Aim for a daily step count of 8,000 to 12,000 steps. This range strikes a balance between sustainability and effectiveness.
Being active doesn’t mean you have to spend hours at the gym. Simple changes to your daily routine can make a big difference. Walk more, take the stairs, or engage in recreational activities.
Finding Your Balance
Be mindful of how much energy you're expending. Too little activity can lead to muscle loss, while excessive activity may lead to burnout. The key is to find a moderate level of activity that you can maintain consistently.
- Use a step tracker to monitor your daily activity.
- Incorporate short bursts of activity throughout your day.
- Engage in activities you enjoy to make staying active fun.
By balancing weightlifting with increased physical activity, you set yourself up for success in achieving your body fat goals.
Strategy Number 3: Eating Nutritiously
Eating nutritiously is essential for achieving and maintaining low body fat. It may seem counterintuitive when your goal is to get lean, but a nutritious diet is crucial. It aligns everything in your favor. You want to keep your gains after you’ve worked hard to get lean.
When you focus on nutritious foods, you’re less likely to revert to unhealthy habits. You won’t go back to eating junk and gaining weight. Eating high-quality foods helps you avoid nutrient deficiencies. It also keeps your energy levels steady and hunger in check.
The Importance of Nutrient Density
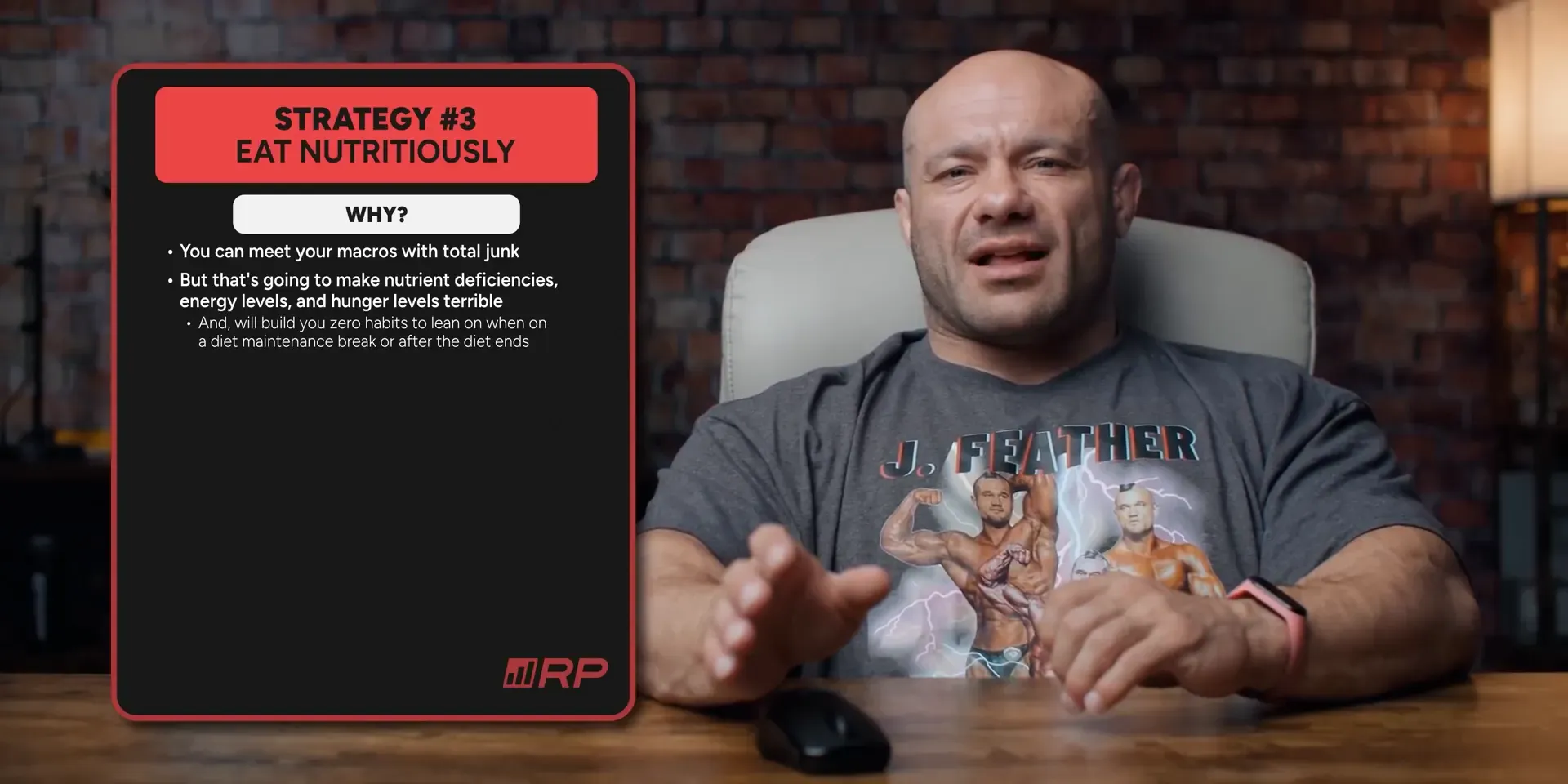
Junk food might meet your macros, but it lacks essential nutrients. This leads to low energy and constant hunger. For instance, eating a half can of Pringles will leave you wanting more shortly after. You won’t feel satisfied.
To stay leaner long-term, build habits around eating nutritious foods. Many people start strict diets but fail to carry those habits forward. They end up swinging between extreme dieting and unrestricted eating.
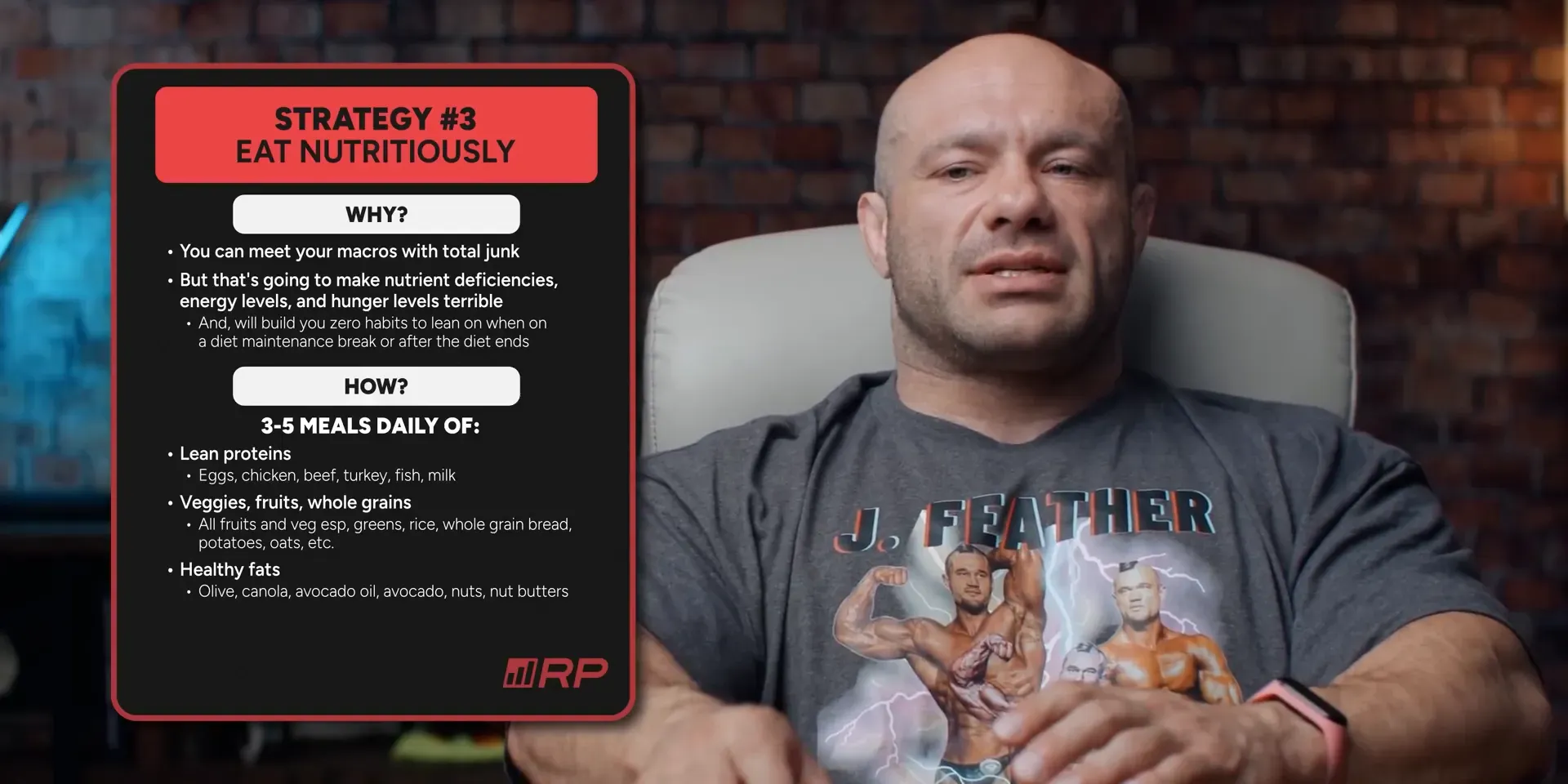
How to Eat Nutritiously
- Consume three to five balanced meals per day.
- Focus on lean proteins: eggs, chicken, turkey, fish, and low-fat dairy.
- Include plenty of vegetables and fruits.
- Incorporate whole grains like rice, oats, and whole grain bread.
- Add healthy fats: olive oil, avocado, nuts, and nut butters.
Your meals should always include protein. You can mix and match carbs and fats based on your needs, but protein must be present in every meal. If you're serious about getting lean, prioritize whole, nutritious foods.
Strategy Number 4: Creating a Caloric Deficit
To lose fat, you must create a caloric deficit. This means consuming fewer calories than your body requires. It sounds simple, but it requires careful planning. You need to know how many calories your body needs to function.
Start by identifying your maintenance calories. From there, aim to eat a few hundred calories less. This deficit will prompt your body to tap into fat stores for energy.
How to Generate a Caloric Deficit
- Lower your fat intake, especially from meats and dairy.
- Switch to leaner cuts of meat, like ground turkey instead of regular beef.
- Opt for low-fat dairy options.
- Once fats are reduced, cut back on carbohydrates, particularly grains.
- Focus on filling your plate with vegetables and fruits.
By making these adjustments, you can significantly reduce your calorie intake without feeling deprived. Aim for a deficit of 250 to 750 calories, depending on your weight and goals.
Monitoring Your Progress
To ensure you're on track, monitor your weight weekly. A loss of 0.5 to 1.5 pounds per week is ideal. If you're losing weight too quickly, it can lead to diet fatigue. If you're not losing, reassess your caloric intake.
Using an app can help track your progress and make adjustments automatically. This takes the guesswork out of your diet and keeps you focused on your goals.
Strategy Number 5: Diet Duration and Breaks
Plan your dieting phases carefully. A typical fat loss phase should last between eight to twelve weeks. This timeframe allows for significant fat loss while minimizing fatigue. Shorter diets can yield quicker results, but they may not be sustainable.
Longer dieting phases can lead to burnout and a drop in motivation. Your body will start to resist the caloric deficit, making it harder to continue losing weight. Recognizing when to take a break is key to long-term success.
When to Take Breaks
- After eight to twelve weeks of dieting, consider a maintenance phase.
- Choose a time in your life with fewer social obligations.
- Allow your body to recover and stabilize.
- Focus on maintaining your weight before starting another dieting phase.
This approach prevents rebound weight gain and keeps your metabolism functioning well. By allowing your body time to adjust, you set yourself up for success in future dieting phases.
Strategy Number 6: Tracking Progress with Weigh-Ins

Weighing yourself regularly is vital. It gives you insight into your progress and helps you make informed decisions about your diet. Weekly weigh-ins provide a clear picture of your trends over time.
Track your weight at the same time each day, or opt for twice a week if daily weighing feels overwhelming. This consistency helps account for fluctuations and gives a more accurate average.
Adjusting Based on Your Weight
- If you're losing weight too quickly, increase your caloric intake slightly.
- If you're not losing, decrease your intake or increase your activity level.
- Use an app for tracking your weight and receiving automatic adjustments.
Staying in tune with your body weight allows you to make necessary adjustments and stay on track toward your goals. Don’t leave your progress to chance; track it diligently.
Strategy Number 7: Managing Diet Fatigue
Diet fatigue is a real challenge for anyone on a fat loss journey. It accumulates over time and can lead to poor results or even a complete diet breakdown. You may find yourself battling intense hunger, low energy, and mood swings. These factors can derail your progress and lead you to make unhealthy choices.
Why Does Diet Fatigue Happen?
Every week in a caloric deficit adds to your diet fatigue. As you lose weight, your body adapts, and the effort required to continue losing becomes greater. This cumulative effect means you need to manage your fatigue proactively to avoid burnout.
Diet fatigue can sneak up on you. You might feel great initially but notice changes as the weeks go by. Your energy dips, cravings increase, and motivation wanes. Recognizing these signs early is crucial.
Strategies to Combat Diet Fatigue
- Weekend Caloric Adjustments: Consider eating a bit more on weekends. Increase your intake by about 500 calories on Friday, Saturday, and Sunday. This allows for social eating and can replenish your energy levels.
- Maintenance Periods: If fatigue becomes overwhelming, take one to two weeks at maintenance calories. This reset can help reduce fatigue while keeping your weight stable.
- Long-Term Planning: After a strict dieting phase, allow for a maintenance or slow gain period. Experts suggest at least two-thirds of the dieting duration in maintenance before starting a new fat loss phase.
These strategies help manage fatigue, allowing you to push harder in future dieting phases without burning out.
Getting Additional Help
Sometimes, you need more than just self-discipline to achieve your goals. Seeking help can significantly enhance your journey. Consider working with a coach or using a specialized app to guide you through the process.
Why a Coach or App?
A coach can provide personalized advice and accountability. They help you navigate challenges and keep you on track. If you prefer a more autonomous approach, an app can serve as your digital guide. It can track your diet, adjust caloric needs, and remind you of your goals.
Both options can simplify your journey and make it more enjoyable. The right support can transform your experience from daunting to manageable.
Expert Corner: Proven Strategies & Hidden Gems
Practical Applications
- Start Small with Weightlifting
Begin your weightlifting routine with just 2 sessions per week. Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses to maximize muscle engagement. Use light weights to perfect your form, then gradually increase the weight as you get stronger. - Track Your Steps Daily
Use a fitness tracker or a smartphone app to monitor your steps. Aim for 8,000-12,000 steps per day by incorporating small changes, such as parking further from entrances, taking short walks during breaks, or opting for the stairs instead of the elevator. - Plan Balanced, Protein-Focused Meals
Prepare meals with at least 20-30 grams of lean protein, like chicken breast or tofu, along with a serving of vegetables and a small portion of whole grains. For example, a grilled chicken salad with quinoa and olive oil dressing is nutritious and filling. - Set a Manageable Caloric Deficit
Calculate your maintenance calories and aim for a 500-calorie deficit per day to lose about 1 pound of fat per week. Use a food-tracking app to log meals and snacks, ensuring you're staying within your target range. - Schedule Maintenance Phases
After 8-12 weeks of dieting, plan a 1-2 week period of eating at maintenance calories. During this time, focus on enjoying balanced meals and allowing your body to recover before resuming fat loss efforts.
Examples
- Increasing Physical Activity: Add a daily 15-minute post-dinner walk to your routine. It could help you hit an extra 2,000-3,000 steps effortlessly.
- Caloric Deficit Meal Plan: Replace a high-calorie lunch (e.g., a burger and fries) with a turkey wrap, mixed greens, and a side of fruit to save 300-400 calories.
Fact-Check of Key Points
- Body Fat Goals and Health
The article mentions single-digit body fat as a goal for men (below 10%) and 17-20% for women. While these are common benchmarks in fitness, achieving and maintaining these levels may not align with optimal health for everyone. Extremely low body fat can disrupt hormonal balance and energy levels, particularly for women aiming for the lower end of the range. Always prioritize overall health alongside aesthetic goals. - Caloric Deficit and Fat Loss
Creating a caloric deficit of 250-750 calories daily is a practical guideline, but the article simplifies the process. Factors like metabolic rate, activity level, and individual body composition can make caloric needs highly variable. Relying solely on generic formulas without considering individual adjustments may lead to underestimating or overestimating calorie needs. - Tracking Progress with Weigh-Ins
Weekly weigh-ins are a helpful strategy, but weight fluctuations due to water retention, hormonal cycles, or muscle gain can skew results. The recommendation to weigh in at the same time daily provides consistency, but pairing weigh-ins with other metrics, like weight trend, body measurements or how clothes fit, can give a more accurate picture. - Diet Fatigue and Breaks
The article advises taking breaks after 8-12 weeks of dieting to reduce fatigue and stabilize progress, which is sound advice. However, the claim that two-thirds of the diet duration should be spent at maintenance could be too rigid. Individual recovery needs and social factors might require a more personalized approach to diet breaks. - Importance of Activity Levels
The suggestion to aim for 8,000-12,000 steps daily is excellent for promoting activity, but it may not suit everyone. Those new to exercise or with time constraints might benefit from starting with smaller goals and progressively increasing their activity.
By considering these nuances, you can approach your fitness goals with a more balanced and sustainable perspective.
More Little-Known Tips for Science-Backed Weight Loss Methods
- Focus on Meal Timing
Adjusting when you eat can enhance your fat loss efforts. For example, consuming more calories earlier in the day and tapering off by evening helps align with your body’s natural rhythms. Start with a protein-packed breakfast and aim to finish your last meal 2-3 hours before bedtime. - Incorporate Active Recovery Days
Recovery is just as important as training. Swap a rest day with an active recovery day by doing light activities like yoga, stretching, or a leisurely walk. This keeps your metabolism humming without adding stress to your body, which is crucial for sustained weight loss. - Stay Hydrated Strategically
Drinking water before meals not only aids digestion but can also reduce calorie intake by helping you feel full faster. Aim for a glass of water 20-30 minutes before each meal. Proper hydration also supports fat metabolism, which is essential for achieving your goals. - Use Protein to Your Advantage
High-protein diets are a cornerstone of weight loss, but spreading your protein intake evenly across meals is key. Aim for 20-30 grams of protein at every meal to maximize muscle preservation and satiety. Snack ideas include a Greek yogurt parfait or a handful of almonds with a boiled egg. - Leverage Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)
Small activities like fidgeting, standing instead of sitting, or even doing housework add up. NEAT can contribute significantly to your daily calorie burn without requiring formal exercise. Set reminders to move for a few minutes every hour to maximize these micro-burns.
Examples of Practical Applications
- Meal Timing: Try eating 40% of your daily calories at breakfast, 35% at lunch, and 25% at dinner for improved energy and weight loss alignment.
- NEAT Boost: Use a standing desk for work or take quick 5-minute walks during phone calls to increase daily calorie expenditure effortlessly.
More Evidence-based Tips for Weight Loss
Sleep Pattern
Maintaining a consistent sleep pattern is crucial for effective weight loss. Poor sleep disrupts hormones that regulate hunger and appetite, leading to increased cravings and overeating. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep daily to support your metabolism and recovery.
Better Lifestyle
Adopting a healthier lifestyle goes beyond diet and exercise. Reduce stress through mindfulness practices, stay hydrated throughout the day, and limit excessive screen time. These small changes can enhance your overall well-being and make your weight loss journey more manageable.
Protein Intake
Increasing protein intake is a proven strategy for fat loss and muscle retention. Aim to include 20-30 grams of protein in each meal from sources like lean meats, eggs, or plant-based alternatives. Protein keeps you full longer and supports recovery after workouts.
Science of Muscle Hypertrophy and Fat Loss
Muscle hypertrophy, or the increase in muscle size, is essential for maintaining strength and metabolism during fat loss. Resistance training, dietary adjustments, and proper program structure play key roles in optimizing hypertrophy while promoting fat reduction.
Key Findings from Research on Muscle Hypertrophy
- Resistance Training Volume and Load
Studies show that resistance training significantly improves muscle mass and strength, with high-load, multiset protocols (e.g., 2-4 sets, ≥70% of 1RM) being effective for muscle growth (Currier et al., 2023). - Frequency of Training
Training muscle groups twice per week results in superior hypertrophy compared to once-weekly protocols. Frequency plays a vital role in maximizing growth when volume is equated (Schoenfeld et al., 2016). - Protein Supplementation
Protein intake enhances resistance training-induced hypertrophy, with optimal effects observed at 1.6 g/kg/day. Beyond this threshold, additional protein provides minimal benefits (Morton et al., 2017). - Training Intensity and Failure
Hypertrophy can be achieved across a range of loads, provided training is performed near muscular failure. High-load training (>80% 1RM) improves strength significantly, while both low- and high-load protocols support hypertrophy (Schoenfeld et al., 2017).
Practical Applications of Science
- Design a Progressive Training Program
Incorporate 2-3 training sessions per muscle group per muscle group, using 10-20 weekly sets focusing on compound lifts. - Optimize Nutrition
Ensure protein intake of 1.6-2.2 g/kg/day and spread consumption evenly across meals to support recovery and muscle growth. - Track and Adjust Training Load
Monitor strength progress and adjust volume or intensity to maintain progressive overload without overtraining.
Scientific Conclusion
Evidence supports structured resistance training, adequate protein intake, and appropriate training volumes and frequencies as effective strategies for muscle hypertrophy during fat loss. Balancing these elements ensures muscle preservation and growth alongside sustained fat reduction.
My Opinion on Science-Backed Weight Loss Methods
I think the science-backed weight loss industry sometimes places too much emphasis on calorie deficits and structured diets, neglecting the importance of psychological and emotional factors. Weight loss isn’t just a numbers game—it’s a mindset. The stress of adhering strictly to calories, macros, and steps often derails more people than it helps.
Some proponents of rigid tracking argue that “what gets measured gets managed.” While I see the merit in accountability, I think it creates a toxic cycle for many. Constantly weighing yourself or tracking every calorie can foster an unhealthy relationship with food and body image. I believe a focus on nourishing your body and staying active, without micromanaging every detail, often leads to better long-term results.
I’m also skeptical of the heavy reliance on apps and coaches to "guarantee" success. While they can provide valuable structure, they sometimes promote dependency. I believe learning to listen to your own body—your hunger cues, energy levels, and progress—is more empowering than outsourcing all your decisions.
In the end, weight loss is personal. I think the best science-backed methods are the ones that fit seamlessly into your lifestyle. They should guide you, not control you. Weight loss should be liberating, not limiting, and the methods you choose should reflect that balance.
The Final Word on Science-Backed Weight Loss Methods
Achieving your weight loss goals doesn’t have to be complicated. By focusing on science-backed weight loss methods like creating a manageable caloric deficit, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, and incorporating strength training, you can build a sustainable lifestyle that supports fat loss and long-term health. The journey is about consistency and making small, impactful changes over time.
Tracking progress, managing diet fatigue, and balancing physical activity can feel overwhelming, but tools like the Dr. Muscle app make it easier. Dr. Muscle automates your workouts, tracks your progress, and adjusts your plan in real-time, ensuring you stay on course. It’s like having a personal coach in your pocket. Try it now with this free trial.
FAQ
What are the most effective science-backed weight loss methods?
The most effective science-backed weight loss methods include creating a manageable caloric deficit of 250-750 calories per day, prioritizing strength training with compound lifts, and incorporating nutrient-dense meals. Tracking progress and planning breaks every 8-12 weeks also contribute to sustainable fat loss.
How can I lose weight naturally according to scientific research?
Losing weight naturally involves combining regular physical activity, such as 8,000-12,000 daily steps, with a diet rich in lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoiding processed foods and focusing on consistency over perfection are also key strategies.
What are some science-backed tips to lose belly fat?
Science-backed tips to lose belly fat include maintaining a caloric deficit, engaging in strength training to preserve muscle mass, and avoiding processed, high-fat foods. Adding physical activity throughout the day, such as walking or taking stairs, can further reduce fat storage around the abdomen.
How can I lose weight fast using scientific methods?
Losing weight quickly with scientific methods requires a focused caloric deficit, high-protein meals, and regular strength training. While fast weight loss is possible, prioritizing sustainability and health by aiming for 0.5-1.5 pounds of weight loss per week is recommended.
What are the best science-backed strategies for sustainable weight loss?
Sustainable weight loss relies on consistency, such as tracking weight weekly, eating balanced meals with lean proteins and vegetables, and exercising regularly. Dieting phases of 8-12 weeks, followed by maintenance periods, help prevent fatigue and promote long-term success.
How can I reduce body fat safely and effectively?
Reducing body fat safely involves maintaining a caloric deficit while consuming nutrient-dense foods and preserving muscle mass through strength training. Regular progress tracking and managing fatigue with periodic breaks are essential for effective fat loss.

